Disclaimer: I am not an EE, nor have I taken any EE classes. This is a cheatsheet, for myself, to remember some of the simple basics of transistors.
Resources
Here are some helpful resources for learning more about the basics of transistors:
| What & Link | Type |
|---|---|
| Zeeshan Ali, AIKTC School of Engineering: Introduction to Transistors | Slide Deck |
| Zeeshan Ali, AIKTC School of Engineering: Transistor Types | Slide Deck |
| ElectronicsTutorials: Transistor Series - Summary (👍) - MOSFET as a Switch |
Guide |
| Circuit Digest: Different Types of Transistors | Guide |
| Espruino: MOSFETs - Schematics section |
Guide (Intro) |
Different Types of Transistors
- BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)
- Control: Current
- Pins:
- Base (B)
- Collector (C)
- Emitter (E)
- Configurations:
- NPN
- PNP
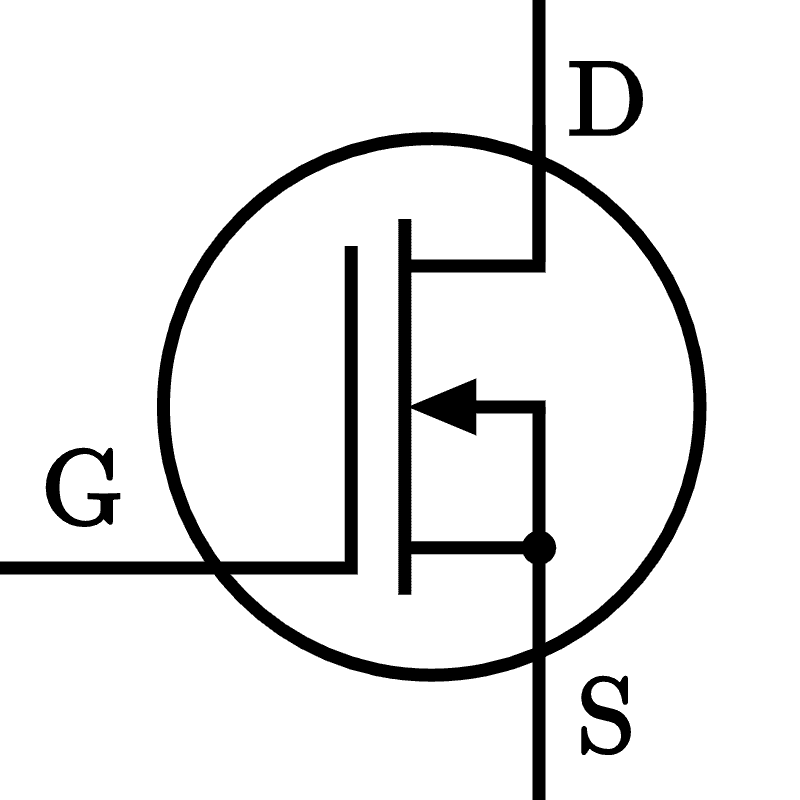
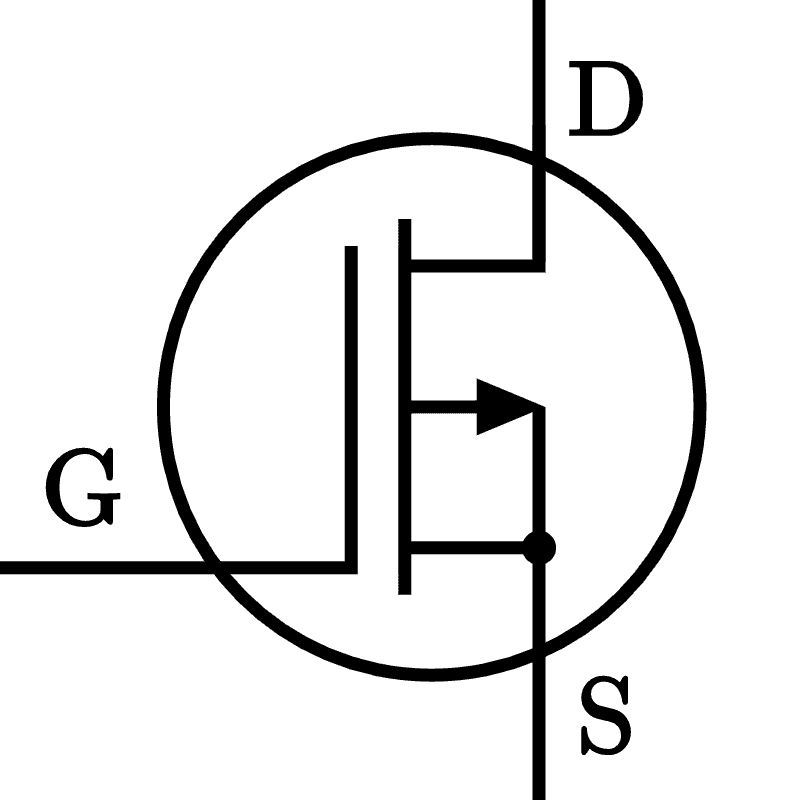
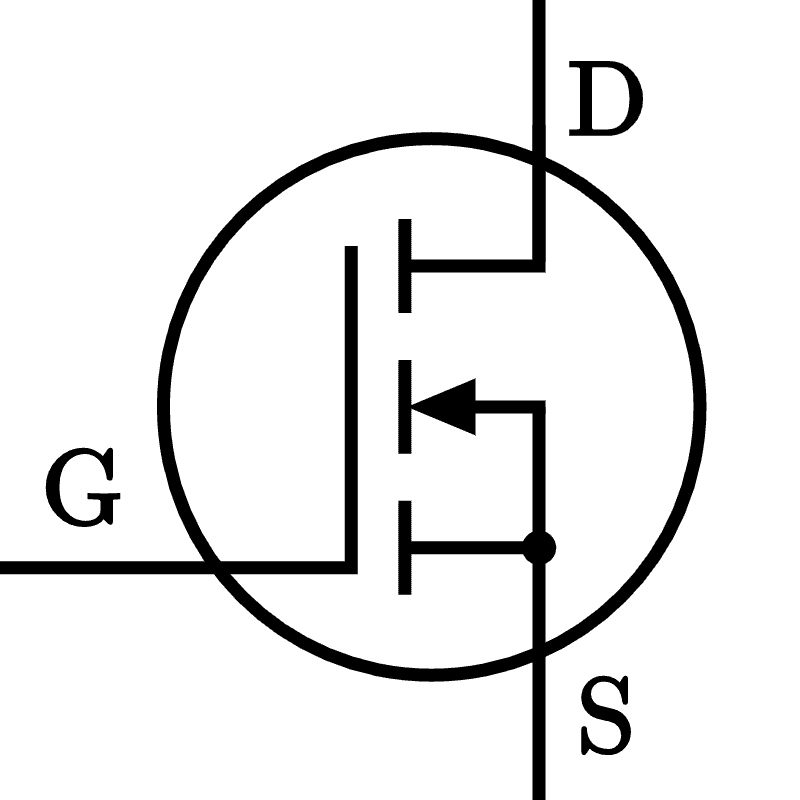
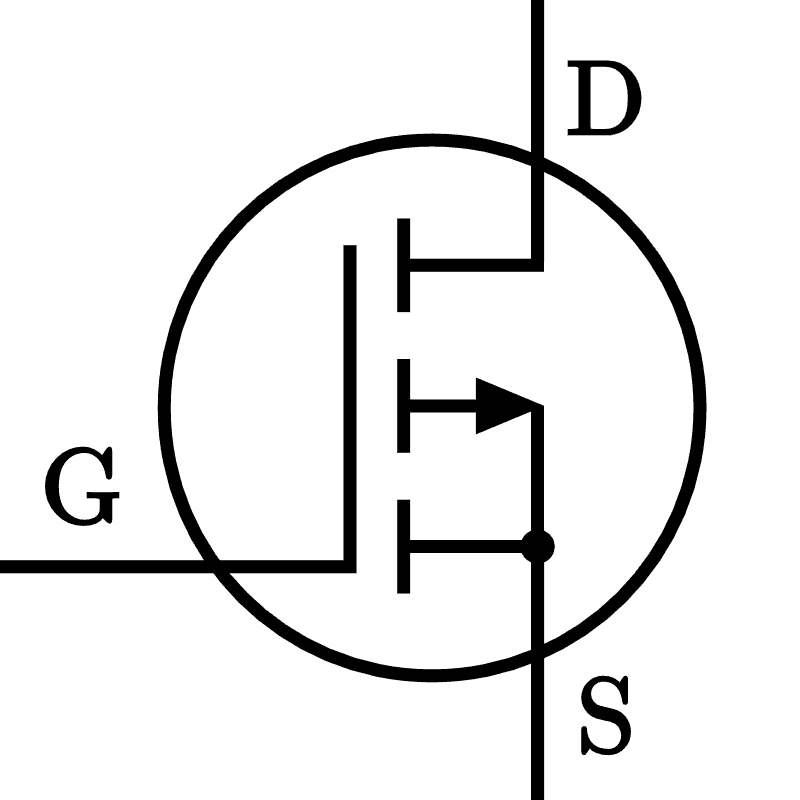
- FET (Field Effect Transistor)
- Control: Voltage
- Pins
- Drain (D)
- Gate (G)
- Source (S)
- Configurations:
- MOSFET
- Depletion Mode:
- N-Channel
- P-Channel
- Enhancement mode:
- N-Channel
- P-Channel
- Depletion Mode:
- JFET
- Depletion Mode:
- N-Channel
- P-Channel
- Depletion Mode:
- OFET
- NOMFET
- MOSFET
- IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)
- This could also be considered a subset of FET
Comparing Types of Transistors
So, between some of the major types, what are the significant differences, in a broad practical sense? As in, why might you pick one over the other?
| Type | Control | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| BJT | Current | - More robust (in comparison to MOSFET) - Often tolerant of a greater voltage range - Less expensive |
- Thermal runaway - Slower switching - Typically handles less current |
| FET - MOSFET | Voltage | - Extremely high input resistance on Gate, means that there is very little current draw - Fast Switching speeds |
- The high input resistance means they are extremely sensitive to ESD, and are more easily damaged by it |
| FET - JFET | Voltage | - Less vulnerable to ESD, compared to MOSFET - Often cheaper than MOSFETs |
- Consumes more current than MOSFET - Only available in Depletion Mode |
Other comparisons you might find helpful
Sub-Type Breakdown
* = Sometimes MOSFETs will include a fourth terminal, B. This is often referred to as Body or Substrate, and sometimes is not broken out, but rather connected internally.